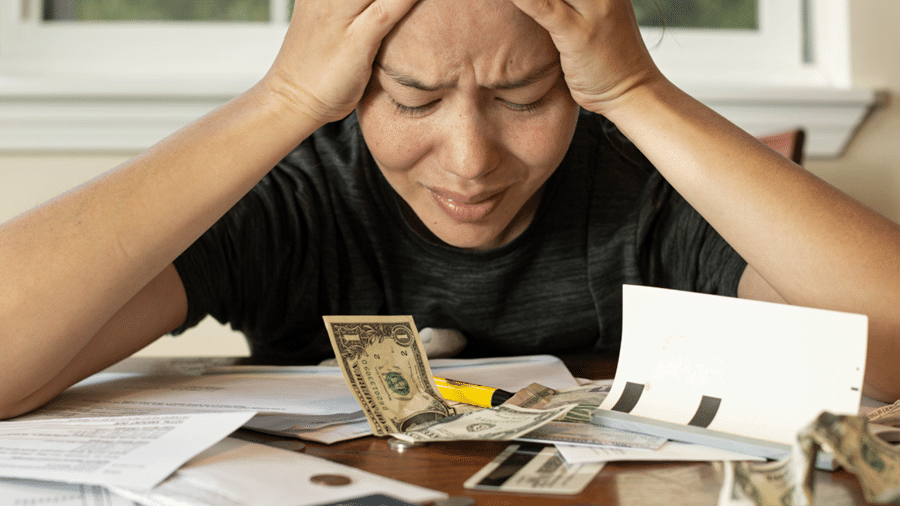
Impulse buying, the spontaneous decision to purchase without prior planning, affects a significant portion of consumer behavior, often driven by psychological factors. These purchases can range from minor treats to substantial investments, leading to immediate satisfaction but potentially adverse long-term financial impacts. This article delves into the psychological underpinnings of impulse buying and provides actionable strategies to curb this instinct. By understanding the triggers and employing targeted techniques, individuals can enhance their financial health and decision-making processes.
Contents
- 1 Understanding Impulse Buying
- 2 Psychological Triggers of Impulse Buying
- 3 The Role of Environment in Impulse Buying
- 4 Impulse Buying and Financial Well-Being
- 5 Recognizing Personal Impulse Buying Patterns
- 6 Strategies to Control Impulse Buying
- 7 Technology and Impulse Buying Control
- 8 Seeking Professional Help for Impulse Buying
- 9 Mastering the Art of Mindful Spending
Understanding Impulse Buying

Impulse buying is characterized by the sudden urge to buy something without premeditation, often resulting in immediate gratification but sometimes regret. This phenomenon differs from planned purchasing, where decisions are made after careful consideration and comparison. Impulse purchases are typically triggered by emotional responses or external stimuli, such as advertising, and are more common with items that are considered luxuries rather than necessities. Understanding these purchases’ nature and triggers is crucial for developing strategies to control such behavior and mitigate its financial implications.
Psychological Triggers of Impulse Buying

Impulse buying is deeply rooted in emotional responses, with feelings like excitement, stress, or even boredom acting as catalysts. Marketing strategies often target these emotions, creating a sense of urgency or exclusivity that prompts immediate action. For instance, the allure of a sale or the fear of missing out (FOMO) can overpower rational thought processes, leading to quick purchases. Recognizing these psychological triggers is the first step toward managing impulsive behavior and making more deliberate and thoughtful purchasing decisions.
The Role of Environment in Impulse Buying

The shopping environment, whether physical or digital, plays a significant role in encouraging impulse purchases. Store layouts, online website designs, and promotional strategies are meticulously crafted to trigger impulsive buying decisions. For example, strategic product placements near checkouts or flashy online pop-up ads can entice consumers to make last-minute purchases. Additionally, social elements, like peer influence or social media trends, can amplify impulsive buying tendencies, illustrating the complex interplay between environment and consumer psychology.
Impulse Buying and Financial Well-Being

Impulse buying can have profound implications for one’s financial health, often leading to unnecessary spending and potential debt accumulation. The immediate satisfaction of an impulse purchase might overshadow the long-term financial consequences, such as depleted savings or increased credit card balances. Chronic impulse buying can disrupt budgeting efforts and financial planning, pushing individuals further away from their financial goals. It’s essential to recognize the financial risks associated with impulsive shopping and to understand that managing these habits can lead to improved financial stability and peace of mind.
Recognizing Personal Impulse Buying Patterns

Identifying personal impulse buying patterns is crucial in developing effective strategies to control it. Self-awareness allows individuals to pinpoint specific triggers, such as emotional states or environmental cues, that lead to spontaneous purchases. By monitoring spending habits and reflecting on past buying decisions, one can uncover patterns and situations that commonly result in impulse buying. This awareness is the foundation for implementing targeted actions to avoid these triggers and establish healthier purchasing habits, ultimately fostering a more mindful and intentional approach to spending.
Strategies to Control Impulse Buying

To mitigate impulse buying, individuals can adopt various practical strategies that promote thoughtful purchasing decisions. Establishing a budget and adhering to a shopping list can create a framework that discourages spontaneous spending. Practicing delayed gratification, where one waits before making a purchase to evaluate its necessity, can also reduce impulsive behaviors. Moreover, mindfulness practices and cognitive exercises can help in developing a more reflective approach to spending, enabling individuals to make purchases that align with their long-term financial and personal goals.
Technology and Impulse Buying Control

Technology offers both challenges and solutions in the realm of impulse buying. On one hand, the ease of online shopping and targeted advertisements can exacerbate impulsive spending behaviors. However, on the other hand, technology also provides tools like budgeting apps and spending trackers that can help individuals manage their finances more effectively. These digital solutions can offer insights into spending patterns, send alerts for unusual purchases, and even block access to certain e-commerce sites, thus serving as a deterrent to impulse buying. Embracing the right technological aids can empower consumers to take control of their spending habits and make more informed purchasing decisions.
Seeking Professional Help for Impulse Buying

When impulse buying becomes a compulsive behavior, it may be time to seek professional help. Financial advisors and psychologists can offer guidance and strategies to individuals struggling with impulse buying, helping them understand the underlying causes and develop effective coping mechanisms. Cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) and other therapeutic approaches can be particularly effective in addressing the psychological aspects of compulsive buying. Professional intervention can lead to significant improvements in financial and emotional well-being, providing the tools needed to establish healthy spending habits and regain control over one’s financial life.
Mastering the Art of Mindful Spending
Impulse buying is a complex behavior influenced by psychological, emotional, and environmental factors. Understanding these aspects is key to developing effective strategies for managing and controlling such spending habits. By recognizing personal triggers, leveraging technology, and possibly seeking professional assistance, individuals can cultivate more mindful and deliberate spending practices. Ultimately, mastering the art of mindful spending not only enhances financial well-being but also contributes to a more intentional and satisfying life.