In today’s digital era, email has become a primary communication tool for both personal and professional correspondence. However, this convenience also brings with it a host of cyber threats. Cybercriminals increasingly leverage email to execute a variety of attacks, ranging from spam to sophisticated phishing schemes. Understanding these threats is crucial for protecting sensitive information. This blog post delves into the various types of cyber threats that can infiltrate inboxes, providing insights and guidance on how to mitigate these risks.
Contents
Spam

Spam emails, often considered a mere nuisance, can be a gateway to more serious cyber threats. Typically, these unsolicited messages flood inboxes with advertisements, but they can also carry harmful content. Some spam emails are crafted to lure recipients into revealing personal information or clicking on malicious links. The danger lies not just in the annoyance they cause but in their potential to serve as a vector for more damaging cyber attacks, such as malware or phishing attempts.
The risks associated with spam are multifaceted. Beyond cluttering the inbox, spam can slow down email servers and compromise network efficiency. More importantly, some spam emails are cleverly disguised to trick recipients into engaging with harmful content. As the sophistication of these deceptive practices increases, so does the challenge of distinguishing spam from legitimate communication. Vigilance and updated spam filters are crucial in mitigating the risks posed by these unwanted emails.
Malware

Malware, a malicious software designed to damage or disrupt systems, often finds its way into systems via email attachments or embedded links. Once opened or clicked, malware can infect computers, leading to data loss, theft, or even complete system takeover. The varieties of malware range from viruses and worms to trojans and ransomware, each with unique characteristics and impacts. Emails have become a favored tool for malware distribution due to their ability to reach a wide audience quickly.
The impact of malware extends beyond individual inconvenience; it poses a significant threat to organizational security. Malware can compromise sensitive data, disrupt business operations, and result in substantial financial losses. The stealthy nature of some malware makes detection and removal challenging, necessitating robust security measures. Regular updates of antivirus software, cautious handling of unknown email attachments, and employee education are essential steps in protecting against malware distributed through emails.
Data Exfiltration
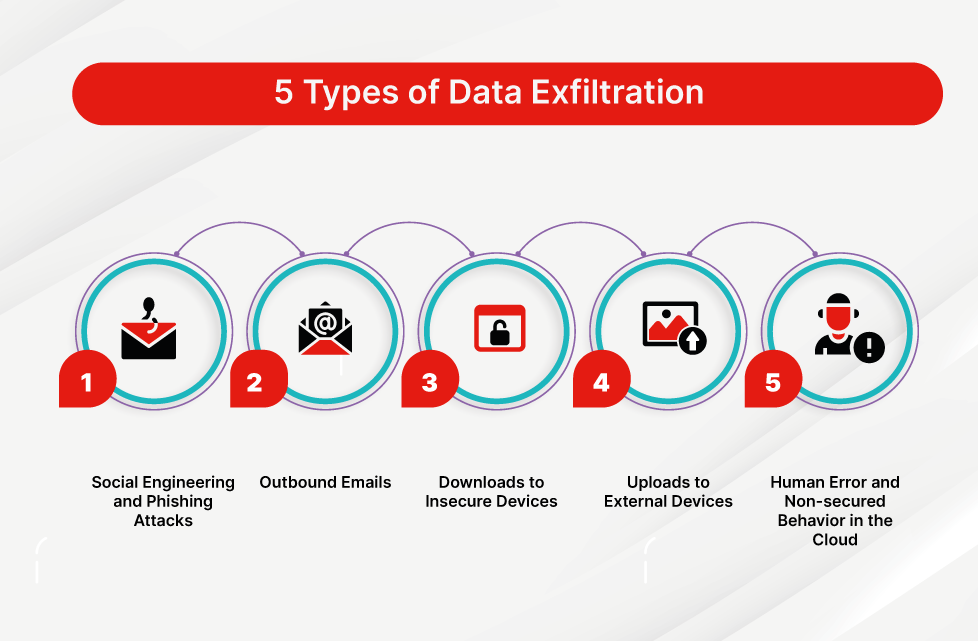
Data exfiltration through email involves unauthorized transfer of sensitive information from a compromised system. Cyber attackers often use sophisticated methods to infiltrate networks and siphon off critical data. These attacks can be executed through malware-infected emails or by gaining direct access to email accounts. Once inside the network, attackers can stealthily extract valuable data over time, leading to significant breaches of privacy and security.
The consequences of such breaches are far-reaching. For individuals, it could mean identity theft or financial loss. For organizations, the ramifications include damage to reputation, loss of customer trust, and potentially hefty legal penalties. Preventing data exfiltration requires a combination of robust cybersecurity measures, employee education, and regular monitoring of network and email activity to detect any unusual patterns that might indicate a breach.
Phishing And Spear Phishing
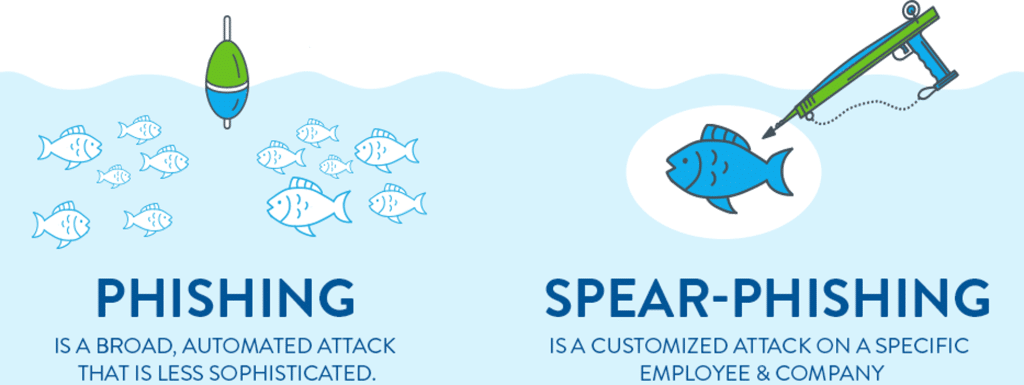
Phishing attacks are deceptive attempts to obtain sensitive information by masquerading as a trustworthy entity in an email. These emails often urge recipients to provide personal information, such as passwords or credit card numbers. Spear phishing, a more targeted form of phishing, involves emails that are tailored to specific individuals, making them more convincing and thus more dangerous.
Despite their prevalence, phishing attacks can be mitigated. Awareness is the first line of defense; knowing how to identify suspicious emails is crucial. Look for red flags like generic greetings, spelling errors, and unfamiliar sender addresses. Technological solutions like anti-phishing software also play a vital role in filtering out these malicious emails. Regular training and simulated phishing exercises can help in keeping individuals vigilant against such attacks.
Ransomware

Ransomware, a type of malware, encrypts a victim’s files and demands a ransom for the decryption key. This form of cyber attack is often distributed via email, with users inadvertently downloading the ransomware by clicking on malicious attachments or links. The aftermath of a ransomware attack can be devastating, as victims lose access to their files and face demands for payment, often with no guarantee of file recovery.
Organizations are particularly vulnerable to ransomware attacks, which can halt critical operations and lead to significant financial losses. To defend against ransomware, it is essential to maintain regular backups of important data. Additionally, updating security systems and software, employing email filters, and educating employees about the dangers of opening suspicious emails are effective strategies to prevent ransomware infections.
Email Spoofing And Identity Theft
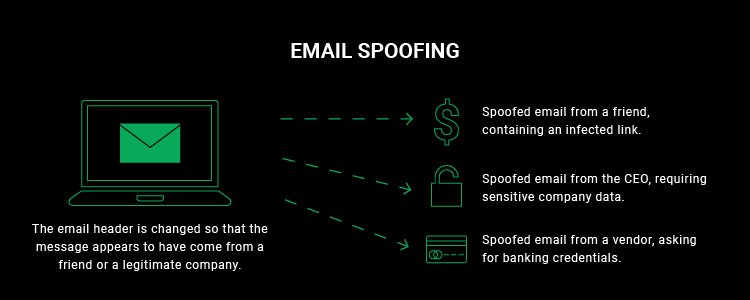
Email spoofing involves the forgery of an email header so that the message appears to originate from someone other than the actual source. This technique is frequently used in phishing attacks to deceive the recipient into trusting the email. Email spoofing can lead to identity theft if individuals are tricked into sharing personal or financial information.
Protecting against email spoofing involves a combination of technical and human solutions. Email authentication protocols like SPF, DKIM, and DMARC can help in verifying the legitimacy of email senders. Users should also be educated to scrutinize email headers, particularly in messages requesting sensitive information. Awareness of the common signs of spoofed emails is critical in preventing identity theft.
Business Email Compromise (BEC)
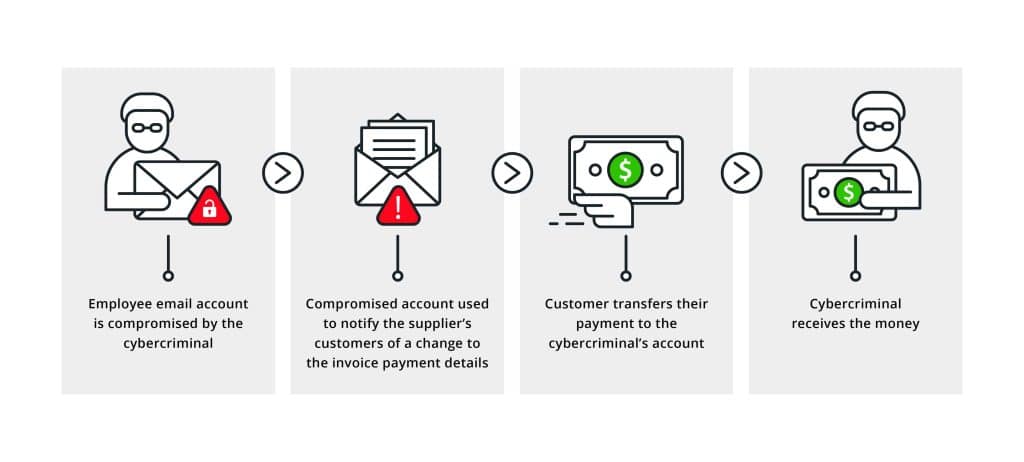
Business Email Compromise (BEC) is a sophisticated scam targeting businesses that regularly perform wire transfer payments. BEC attacks often involve compromising legitimate business email accounts through social engineering or computer intrusion techniques. Once an attacker gains access, they can impersonate company executives or vendors to request fraudulent transfers of funds.
Preventing BEC requires a multi-faceted approach. Organizations should implement strong internal controls on financial transactions, such as secondary verification methods for wire transfer requests. Training employees to recognize the signs of BEC and maintaining robust cybersecurity measures, including two-factor authentication for email accounts, can significantly reduce the risk of these costly scams.
The Bottom Line
Navigating the landscape of cyber threats in email requires constant vigilance and a proactive approach. From spam to sophisticated BEC scams, these threats pose significant risks to personal and organizational security. Implementing robust cybersecurity measures, educating individuals about the signs of email-based threats, and maintaining regular backups are key to safeguarding against these risks. The key takeaway is clear: in the digital age, awareness and preparedness are paramount in protecting against the myriad of cyber threats lurking in inboxes.