Every day, whether at home, in the office, or outdoors, we are exposed to a myriad of airborne toxins, often without realizing it. These invisible threats, ranging from indoor pollutants to outdoor emissions, can have a significant impact on our health. This article delves into the world of airborne toxins, exploring their sources, types, and the health risks they pose. By understanding what these toxins are and where they come from, we can take informed steps to protect ourselves and improve the air quality around us.
Understanding Airborne Toxins
Airborne toxins are substances in the air that can have detrimental effects on human health. They include a wide range of particles, gases, and biological molecules that originate from various sources, such as industrial processes, vehicle emissions, and natural events. These toxins can cause immediate health problems like respiratory distress, and in the long term, they may contribute to chronic diseases. Understanding the nature and origin of these substances is crucial for developing effective strategies to minimize their impact on our health.
The presence of airborne toxins is not limited to outdoor environments; they can be equally prevalent indoors. Common sources in our homes and workplaces include building materials, household cleaning agents, and even some personal care products. The effects of these toxins depend on their concentration and the duration of exposure. Recognizing these sources is the first step in reducing our exposure and protecting our health.
Common Indoor Air Pollutants

Indoor air quality is often overlooked, yet the air inside homes and buildings can be more polluted than outdoor air. Common indoor air pollutants include formaldehyde, found in furniture and building materials; radon, a natural radioactive gas that can enter buildings from the ground; and volatile organic compounds (VOCs) emitted from paints, cleaning supplies, and air fresheners. These pollutants can cause a range of health issues, from eye irritation and headaches to more serious respiratory and cardiovascular diseases.
Detecting and controlling these indoor pollutants is essential for maintaining healthy indoor air quality. Regular testing for radon, proper ventilation, and choosing low-emission products can significantly reduce the levels of these toxins. Awareness of the potential sources and health effects of indoor air pollutants is key to creating safer indoor environments.
Contents
Outdoor Air Pollution
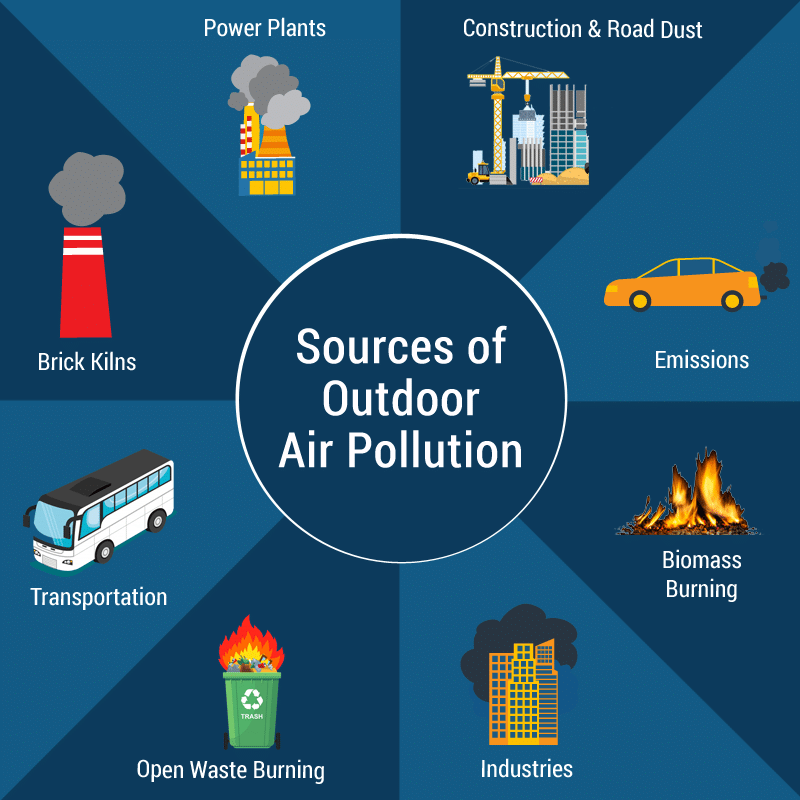
Outdoor air pollution is a major environmental health risk, particularly in urban areas. Common pollutants include particulate matter from vehicle exhausts, smoke, and industrial emissions, as well as nitrogen oxides and sulfur dioxide from burning fossil fuels. These pollutants can have immediate effects like exacerbating asthma and long-term consequences such as increasing the risk of cardiovascular diseases and lung cancer.
The quality of outdoor air varies greatly between urban and rural areas, with cities often experiencing higher levels of pollution due to dense traffic and industrial activities. Understanding the impact of outdoor air pollution is vital for implementing policies and practices to improve air quality. Measures such as promoting public transportation, regulating industrial emissions, and planting urban greenery can play a significant role in reducing outdoor air pollution and its associated health risks.
The Impact of Agriculture and Pesticides
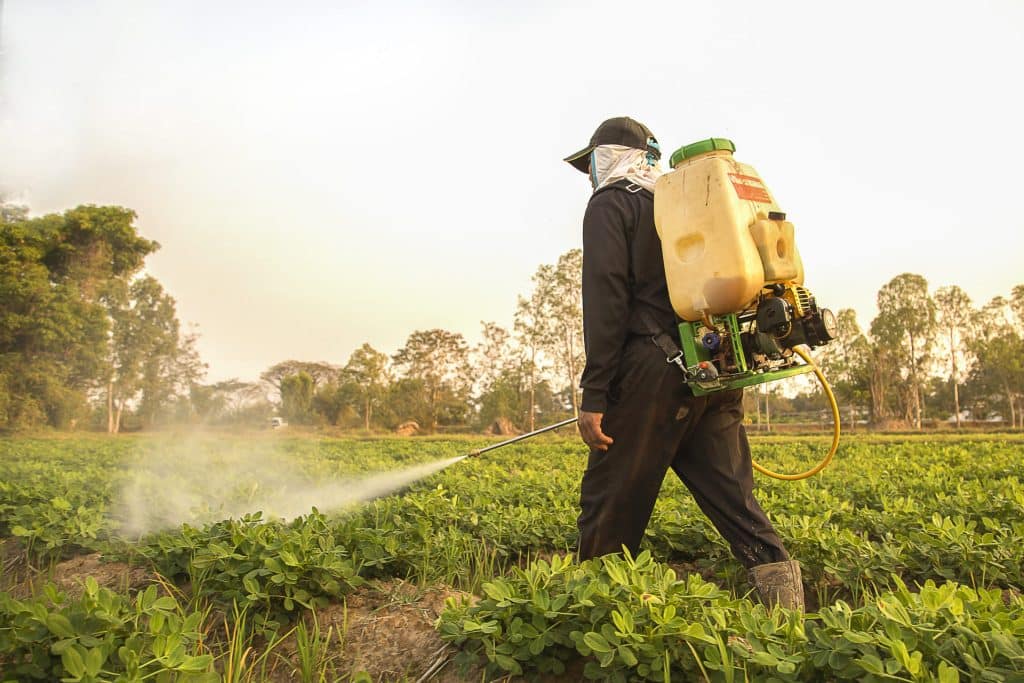

Agriculture, though often associated with feeding the population and rural tranquility, is also a significant source of airborne toxins. Pesticides and fertilizers used in farming can become airborne, spreading beyond their intended targets and impacting air quality. This dispersion can occur through drift during application, evaporation, or dust particles attaching to these chemicals. The effects of these airborne agricultural chemicals range from potential respiratory issues to more severe health risks, especially in communities close to agricultural areas.
The types of pesticides prevalent in the air include insecticides, herbicides, and fungicides, each with its specific health risks. The extent of their spread and impact depends on factors such as weather conditions, application methods, and the types of chemicals used. Monitoring air quality in agricultural areas and using safer, more sustainable farming practices can help reduce the release of these toxins. Public awareness and regulation of pesticide use are also crucial in minimizing the impact of agricultural airborne toxins on the environment and public health.
Effects of Airborne Toxins on Health

Exposure to airborne toxins can have a wide range of effects on human health, varying from mild to severe. Short-term exposure can lead to immediate symptoms like coughing, eye irritation, and headaches. Long-term exposure, however, can be more detrimental, potentially leading to chronic respiratory conditions, cardiovascular diseases, and even cancer. Vulnerable populations, such as children, the elderly, and individuals with pre-existing health conditions, are particularly at risk from these toxins.
Studies and research have continuously highlighted the correlation between airborne toxins and health issues. For example, prolonged exposure to fine particulate matter (PM2.5) has been linked to an increased risk of heart attacks and aggravated asthma. Understanding these health effects is critical for both individuals and policymakers to take action in reducing exposure and implementing protective measures. Public health campaigns and education can play a significant role in raising awareness of these risks.
Regulatory Standards and Air Quality Monitoring

Regulatory standards play a vital role in controlling and minimizing the impact of airborne toxins. Organizations like the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) in the United States set guidelines and limits for air pollutants to protect public health. These regulations cover a wide range of toxins, including industrial emissions, vehicle exhaust, and indoor pollutants. The effectiveness of these regulations is essential in ensuring safer air quality for the population.
In addition to regulations, air quality monitoring is crucial for understanding and managing air pollution. Monitoring stations provide real-time data on air quality, tracking pollutants like particulate matter, nitrogen dioxide, and ozone. This data is used to inform the public about current air quality conditions and to guide policy decisions on air quality management. Increased investment in air quality monitoring and continuous refinement of regulatory standards are key to effectively combating air pollution and protecting public health.
Personal and Public Measures to Reduce Exposure

Individual actions play a crucial role in reducing exposure to airborne toxins. In homes and workplaces, simple steps like using air purifiers, ensuring proper ventilation, and choosing natural cleaning products can significantly decrease the concentration of indoor pollutants. Regular maintenance of HVAC systems and using indoor plants are also effective in improving air quality. Additionally, being aware of outdoor air quality forecasts can help individuals plan their activities to avoid high pollution levels, especially for those with respiratory conditions.
On a public scale, initiatives and policies are essential in addressing air pollution. Governments and local authorities can implement regulations to limit emissions from vehicles and industrial plants, promote the use of renewable energy, and enhance public transportation options. Urban planning that includes green spaces and tree planting can also contribute to cleaner air. Community involvement in environmental programs and supporting policies aimed at reducing air pollution are vital steps in making a collective impact on air quality.
The Future of Air Quality and Public Health

The future of air quality and its impact on public health is a subject of increasing concern and attention. Advances in technology, such as the development of more efficient air filtration systems and the use of big data for air quality monitoring, offer promising tools for improving air quality. Research into sustainable practices and renewable energy sources is also critical in reducing the reliance on pollution-heavy processes. The role of emerging technologies in addressing air quality issues is an area of potential growth and innovation.
Public awareness and education are equally important in shaping the future of air quality. As individuals become more informed about the sources and effects of airborne toxins, their demand for cleaner air and support for environmental policies is likely to increase. This shift in public consciousness, combined with technological advancements and stronger regulatory frameworks, will be key in driving efforts to improve air quality and protect public health. The collaboration of various sectors—government, industry, science, and the public—is crucial for making sustainable improvements in air quality and public health outcomes.
Breathing Easier
It’s clear that airborne toxins present a significant challenge to our health and environment. This post has explored various aspects of air pollution, from indoor pollutants to the broader impacts of agriculture and industrial emissions. Understanding these challenges is the first step towards mitigating their effects. Each one of us has a role to play, whether it’s through personal actions to improve indoor air quality or supporting public initiatives for cleaner air. The journey towards better air quality requires combined efforts from individuals, communities, and policymakers. Together, we can create a future where we all breathe easier and live healthier lives.