The trend of reducing meat consumption has gained significant momentum in recent years, driven by growing awareness of its numerous benefits. From improving personal health to mitigating environmental impact and addressing ethical concerns, the reasons for cutting down on meat are compelling. This article delves into the multifaceted advantages of reducing meat intake, providing a comprehensive overview of how such a dietary shift can lead to a healthier, more sustainable, and ethically conscious lifestyle. Understanding these benefits can inspire and empower individuals to make informed choices that positively impact their well-being and the world around them.
Contents
- 1 Health Benefits
- 2 Nutrient Intake
- 3 Chronic Disease
- 4 Weight Management
- 5 Environmental Benefits
- 6 Reduced Greenhouse Gas Emissions
- 7 Conservation of Resources
- 8 Ethical Considerations
- 9 Animal Welfare
- 10 Reduction in Animal Suffering
- 11 Economic Advantages
- 12 Cost Savings
- 13 Market Growth
- 14 Personal Well-being
- 15 Mental Health
- 16 Energy Levels
- 17 Social and Cultural Impact
- 18 Changing Food Culture
- 19 Community Benefits
- 20 Practical Tips for Reducing Meat Consumption
- 21 Gradual Transition
- 22 Educational Resources
- 23 Embracing a Healthier and More Sustainable Lifestyle
Health Benefits

Nutrient Intake
Reducing meat consumption often leads to a greater intake of fruits, vegetables, and whole grains, which are rich in essential nutrients. These plant-based foods provide higher levels of vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants compared to a meat-centric diet. Consuming a variety of these foods ensures a balanced intake of nutrients that support overall health. Additionally, a plant-based diet is typically higher in fiber, promoting better digestion and contributing to improved gut health.
Chronic Disease
One of the most significant health benefits of reducing meat consumption is the lower risk of chronic diseases. Diets high in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains have been shown to reduce the risk of heart disease, hypertension, and type 2 diabetes. Studies also indicate a correlation between reduced meat intake and a decreased risk of certain cancers, particularly colorectal cancer. By minimizing meat consumption, individuals can significantly enhance their long-term health and reduce the likelihood of developing serious health conditions.
Weight Management
Switching to a diet with less meat can aid in weight management and help maintain a healthier body mass index (BMI). Plant-based foods generally have fewer calories and lower fat content compared to meat, making it easier to control calorie intake. This dietary change often leads to weight loss and improved fitness levels, as well as a decrease in obesity-related health issues. The emphasis on nutrient-dense foods also promotes better overall health and well-being, contributing to a more active and energetic lifestyle.
Environmental Benefits

Reduced Greenhouse Gas Emissions
The environmental impact of meat production is profound, particularly concerning greenhouse gas emissions. Livestock farming is a significant contributor to CO2, methane, and nitrous oxide emissions, all of which are potent greenhouse gases. By reducing meat consumption, individuals can lower their carbon footprint, as plant-based diets generate significantly fewer emissions. This shift is crucial for mitigating climate change and promoting environmental sustainability.
Conservation of Resources
Meat production is resource-intensive, requiring large amounts of water, land, and feed. In contrast, plant-based food production is much more efficient, using fewer resources and causing less environmental degradation. Reducing meat consumption helps conserve water and reduce deforestation, as less land is needed for livestock farming. This conservation effort not only protects ecosystems and biodiversity but also promotes more sustainable land use practices.
Ethical Considerations
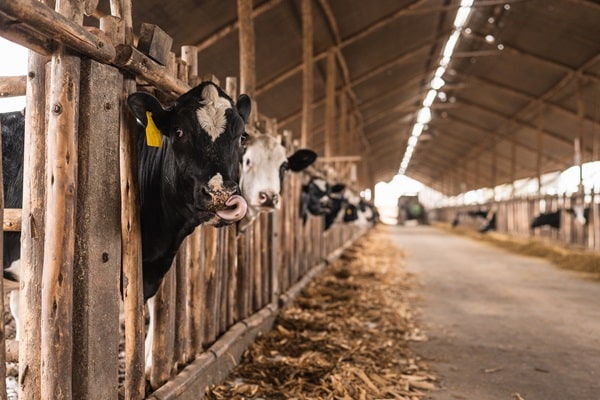

Animal Welfare
One of the primary ethical concerns associated with meat consumption is the welfare of animals. Factory farming practices often involve crowded, inhumane conditions that cause significant suffering to animals. Reducing meat intake supports more humane farming practices and reduces the demand for factory-farmed meat. By choosing plant-based options, individuals can contribute to a more ethical food system that prioritizes animal welfare and humane treatment.
Reduction in Animal Suffering
Lowering meat consumption directly impacts the number of animals raised in harsh conditions. With decreased demand for meat, fewer animals are subjected to the cruelty of factory farming. This reduction in animal suffering is a compelling reason for many to consider a plant-based diet. Ethical eating involves making choices that align with values of compassion and respect for all living beings, and reducing meat consumption is a significant step in that direction.
Economic Advantages

Cost Savings
Reducing meat consumption can lead to significant cost savings, as plant-based foods are often less expensive than meat. Purchasing vegetables, fruits, grains, and legumes in bulk is typically more affordable than buying meat, especially cuts of high-quality or organic meat. Home-cooked plant-based meals further maximize savings by minimizing the need for costly processed foods or dining out. Over time, these savings can add up, providing more financial flexibility for individuals and families.
Market Growth
The growing popularity of plant-based diets has spurred economic opportunities within the food industry. Companies that produce plant-based alternatives and sustainable agriculture products are experiencing rapid growth and innovation. This market expansion creates jobs and stimulates economic activity in sectors related to alternative proteins, plant-based foods, and sustainable farming practices. Supporting these industries not only benefits consumers but also drives positive economic change.
Personal Well-being

Mental Health
Adopting a diet with less meat can positively affect mental health and emotional well-being. Diets rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains have been linked to lower levels of anxiety and depression. The nutrients found in plant-based foods, such as vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants, support brain health and can improve mood and cognitive function. Making mindful dietary choices can enhance mental clarity and overall emotional stability.
Energy Levels
Plant-based diets can boost energy levels and overall vitality. Nutrient-dense plant foods provide sustained energy without the heaviness often associated with meat-based meals. Improved digestion from a high-fiber diet also contributes to feeling more energized and less sluggish. This increase in energy can lead to better productivity, enhanced physical performance, and a greater sense of well-being throughout the day.
Social and Cultural Impact

Changing Food Culture
The shift towards reducing meat consumption is influencing food culture worldwide. Vegetarian and vegan diets are becoming more mainstream, with a growing number of people embracing these lifestyles for health, ethical, and environmental reasons. Social media and celebrity endorsements play a significant role in promoting plant-based diets, making them more appealing and accessible to a broader audience. This cultural shift is fostering a more inclusive and diverse food landscape.
Community Benefits
As more people reduce their meat consumption, the availability of plant-based options in restaurants, grocery stores, and markets has increased. This shift supports local farmers and businesses that focus on sustainable and ethical food production. Communities benefit from having greater access to healthy, affordable, and environmentally friendly food choices. Additionally, this movement encourages communal support and shared experiences around plant-based eating, strengthening social bonds and promoting a collective sense of well-being.
Practical Tips for Reducing Meat Consumption

Gradual Transition
Making a gradual transition to a diet with less meat can help ease the process and ensure long-term success. Start by implementing Meatless Mondays or choosing a few days a week to focus on plant-based meals. Experiment with new recipes and explore different cuisines that emphasize vegetables, grains, and legumes. Incorporating plant-based substitutes for your favorite meat dishes can also make the change more enjoyable and less daunting.
Educational Resources
Utilizing educational resources can provide guidance and support for reducing meat consumption. Cookbooks, blogs, and online courses offer a wealth of information on plant-based cooking and nutrition. Joining support groups or online communities can also be beneficial, as they provide a platform to share experiences, recipes, and tips. These resources can help individuals stay motivated and informed as they navigate their journey toward a more plant-based diet.
Embracing a Healthier and More Sustainable Lifestyle
The benefits of reducing meat consumption are vast, impacting personal health, the environment, ethical considerations, and the economy. By embracing a diet rich in plant-based foods, individuals can enjoy improved well-being, contribute to environmental conservation, and support ethical farming practices. The cultural shift towards plant-based diets also fosters community growth and economic opportunities. Gradually reducing meat intake with the help of educational resources can make the transition smoother and more sustainable. Making informed dietary choices can lead to a healthier lifestyle and a more sustainable world for future generations.